Heart Treatments
Cardiac Angioplasty & Stenting
1. Why is Coronary Angioplasty and Stenting performed?
Coronary angioplasty and stenting are procedures that open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries.
These are performed to check if a coronary artery is blocked, to assess how severe the blockage(s) are and to treat the problem using a catheter.
2. How is this procedure performed?
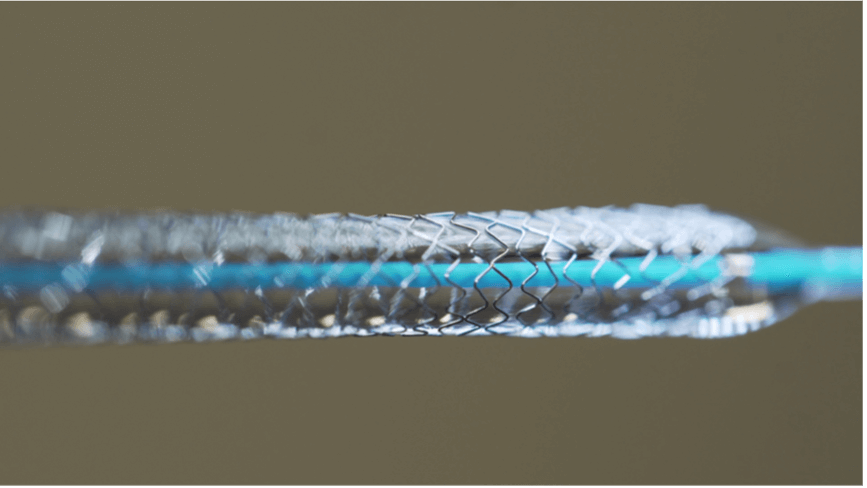
During this procedure, your doctor will widen your blocked artery using a small tube called a catheter. The catheter will have a balloon at the end of it and this is inserted into the coronary arteries through the groin or arm.
Your doctor will then inflate the balloon in the blocked artery to move the plaque causing the blockage, which will improve the blood flow. A mesh tube called a stent is then placed in the widened artery to keep it open
This procedure uses x-ray imaging to visualise the hearts blood vessels and it is performed to check if there is a restriction impacting the blood flow going to your heart.
3. What type of symptoms would a person be experiencing to be referred for this procedure?
Some of the symptoms that may indicate the need for a Coronary Angioplasty or stenting to be performed may include;
- Chest pain (angina)
- Pain in your jaw, neck, arm or leg which is unexplained by other tests
- Swelling or skin changes
- Shortness of breath and fatigue
- A heart value problem or abnormal results from a stress test, electrocardiogram or echocardiogram